AI's New Frontier: Reimagining Your Terminal with Intelligent Agents
Rethinking the Command Line with AI
The terminal—long hailed as the developer’s power tool—has historically required an intimidating level of expertise. It demanded precise syntax, obscure flags, and near-religious mastery of text-based commands. But that era is evolving rapidly. AI is now embedding itself into the command-line interface (CLI), transforming it from a memorization gauntlet into an intuitive, intent-driven experience.
This change marks a deeper transformation: instead of focusing on how to do something, developers can now focus on what they want to achieve. It’s a major leap forward in developer experience, onboarding, and productivity—lowering the barrier for beginners and supercharging experts.
In this article, we examine three next-gen AI tools reimagining the terminal: Google Gemini CLI, Arkterm, and Warp.dev. Each offers a unique take on the AI-powered development environment, from large-context agents to fast command assistants and full multi-agent orchestration.
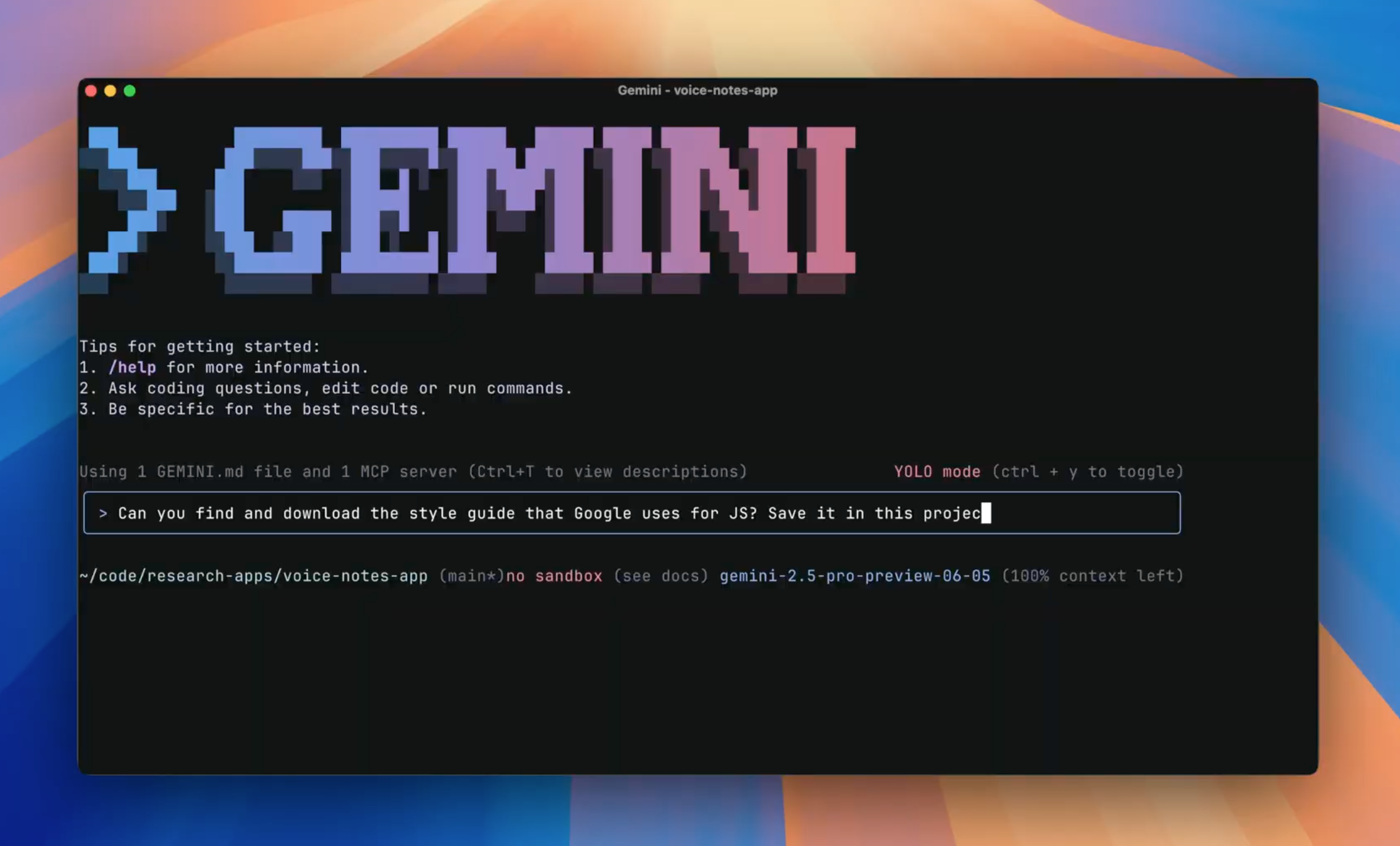
Google Gemini CLI: Your AI-Powered Terminal Assistant
The Gemini CLI from Google brings Gemini 1.5 Pro’s capabilities directly to the terminal. With its massive 1 million-token context window, it can reason over entire codebases, conversations, or documentation.
Key Features:
- Natural Language Interface: Ask it to generate code, fix bugs, or research APIs.
- Search Grounding: Integrates live Google Search results into its responses.
- Script-Friendly: Works in both interactive and non-interactive (scripted) modes.
- Open Source: Licensed under Apache 2.0 and open to community contributions.
- Generous Free Tier: 60 requests/minute and 1,000/day—free with a Google account.
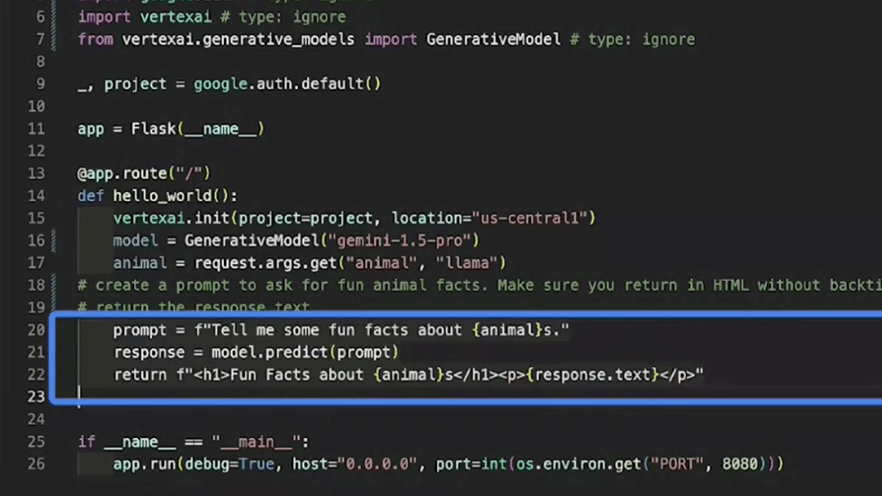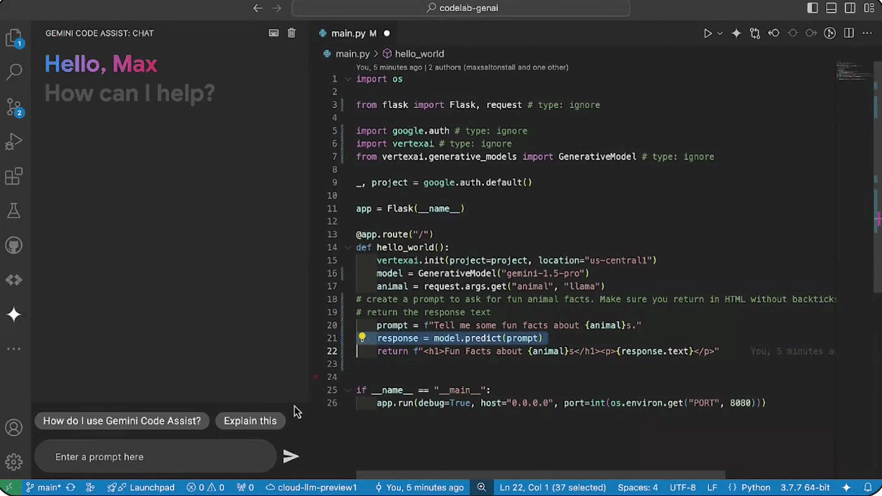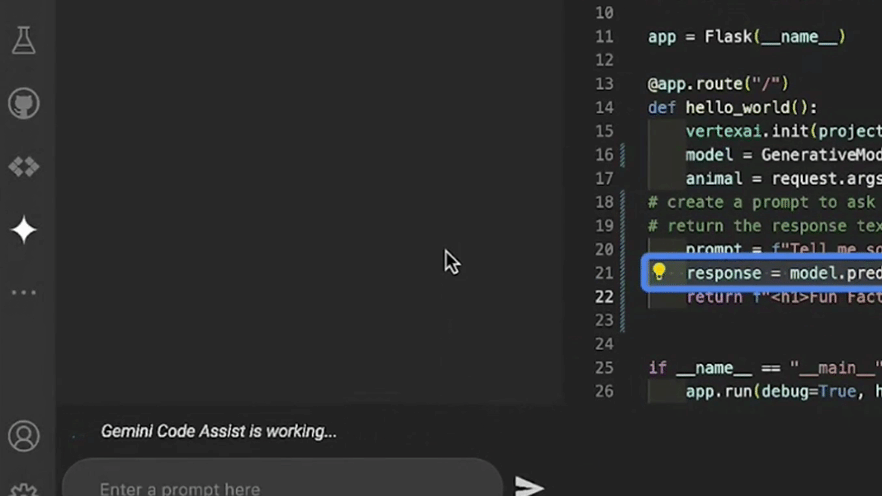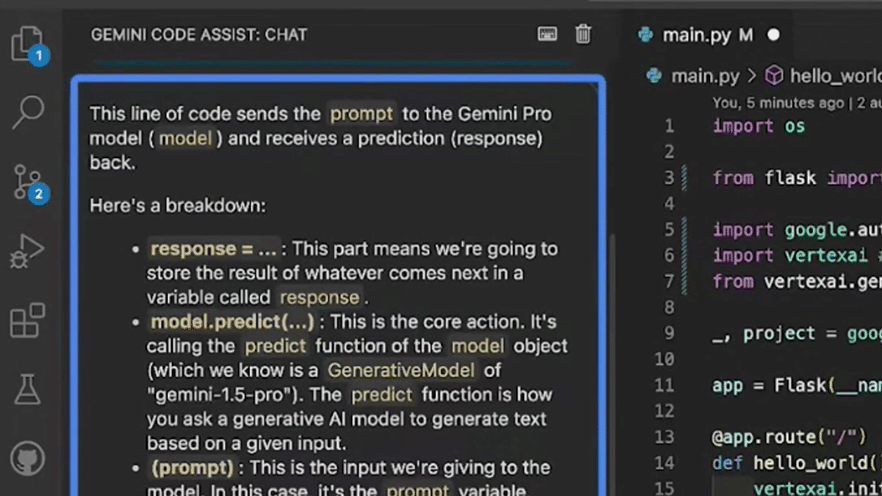
Developers can provide custom context via Model Context Protocol (MCP) to tailor results to a project or company stack. It also shares functionality with Gemini Code Assist in VS Code, enabling multi-step plans, recovery from failures, and more.
ArkTerm: Fast, Safe, and Linux-Centric
ArkTerm is a lightweight, safety-first assistant for Linux users that translates natural language into precise CLI commands using LLAMA 3.1 via Grok’s LLM API.
What Sets It Apart:
- Sub-Second Responses: Delivers rapid results essential for terminal workflows.
- Command Safety: Never auto-executes commands. Warns users of destructive operations like rm -rf.
- Context-Aware: Detects your current directory/project type (e.g., Python, Rust) to fine-tune suggestions.
- Interactive Mode: Conversational follow-ups in-session.
- Whether you’re a sysadmin trying to compress logs or a dev managing Git repos, Arkterm reduces the time spent googling flags or parsing man pages—making Linux more approachable without sacrificing control.
Warp.dev: Terminal as a Multi-Agent Workspace
Warp.dev pushes the boundaries further by evolving the terminal into a multi-agent development environment. Rather than a single assistant, Warp uses multiple coordinated agents that collaborate across tasks.
Agentic Workflow:
- Tell: Express your goal in natural language.
- Agents Write: Different agents generate and modify code across repos.
- Run in Parallel: Multiple agents execute workflows—debugging, building, deploying—all at once.
Warp’s Enterprise-Level Capabilities:
- Warp Drive & MCP: Share knowledge between agents for cohesive execution.
- Security First: BYO LLM, Zero Data Retention, and step-level user control.
- End-to-End Automation: From building full-stack apps to fixing bugs linked from Linear, Warp handles complete development lifecycles.
This agentic model hints at a near-future where developers orchestrate AI teams like engineers lead human ones—delegating tasks while maintaining high-level oversight.
Final Thoughts: The Terminal Becomes a Collaborator
AI-powered terminals mark a shift in how we write, test, and deploy code. Whether you prefer the raw power of Gemini CLI, the speed and safety of Arkterm, or the orchestration of Warp.dev, one thing is clear: the terminal is no longer just a tool—it’s becoming a partner.
This evolution could fundamentally reshape the path into software development. Learning to code might start with learning to communicate with AI agents rather than memorizing Bash syntax. That means more access, faster learning, and ultimately—smarter software development.
Welcome to the AI-native command line.